Be your Logistics Department in China
Customized logistics solutions, your logistics expert in China
Customized logistics solutions, Shipping from China to the World
Tel:+8613424475220 Email:info@viputrans.com 
Lithium-ion batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that have become widely used in various electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and even grid energy storage systems.
They are named after the lithium ions that move between the battery's two electrodes during charging and discharging.
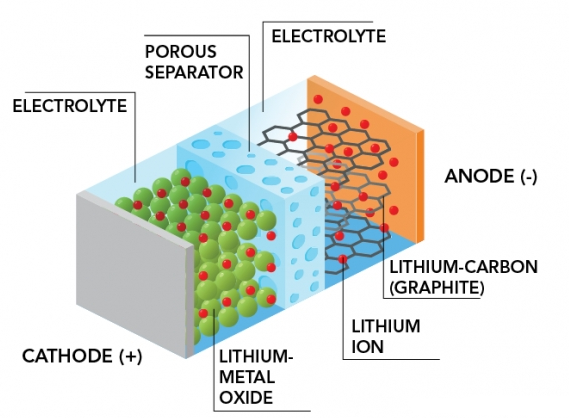
Cathode: The cathode is the positive electrode of the battery and is typically made of a lithium compound, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), or lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4). The cathode attracts and stores lithium ions during charging.
Anode: The anode is the negative electrode and is typically made of graphite, which allows for the intercalation of lithium ions during charging. Graphite anodes have a high capacity to store lithium ions, which contributes to the battery's overall energy density.
Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a chemical compound that allows the flow of lithium ions between the cathode and anode while providing electrical insulation. It is usually a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent.
Separator: The separator is a permeable membrane that prevents direct contact between the cathode and anode. It keeps the electrodes apart while allowing the movement of lithium ions.
The types of materials may differ in these batteries, offering varying levels of power, energy, cost, performance and lifespan, but they all function as Li-ion power sources.
Lithium cobalt oxide: This battery typically appears in mobile phones and laptops due to its low cost and moderate power delivery.
Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide: Electric bikes and vehicles typically use this type of Li-ion battery.
Lithium iron phosphate: Due to its high safety level and long life, this battery type often appears in electric motorcycles.
Lithium manganese oxide: Though low in cost, this type of Li-ion battery also has a relatively short lifespan compared to others. It often has applications in power tools and medical devices.
Lithium titanate: A costly battery that offers great performance, long life and a high level of safety, this type of cell often appears in smart grids and for storing solar panel energy.
Lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide: With a moderate lifespan and similar performance level, this form of Li-ion battery often powers electric powertrains.

Related to these power supplies are lithium metal batteries, also known as primary batteries or non-chargeable lithium batteries.
While you can ship both of these types of power sources, you must take special precautions to prevent them from shorting and catching on fire during transit.
During charging, lithium ions flow from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte, where they are stored in the graphite structure.
When the battery is in use, the lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode, creating an electric current that powers the device.

Lithium-ion batteries have several advantages over other types of rechargeable batteries. They have a high energy density, which means they can store a relatively large amount of energy in a compact size.
They also have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can hold their charge for extended periods when not in use.
Additionally, lithium-ion batteries have a long cycle life, allowing them to be recharged and discharged many times before their performance significantly degrades.
Li-ion batteries use several materials inside them as the electrolyte to transport the lithium ions between the cathode and anode. Most of these electrolytes have flammable, irritating or toxic properties, making transporting them potentially dangerous.
1,2 Diethoxyethane: Flammable and toxic
1,2 Dimethoxyethane: Flammable and toxic
1,3 Dioxolane: Flammable
y-Butyrolactone: Harmful
Diethyl carbonate: Flammable
Dimethoxymethane: Flammable and irritating
Dimethyl carbonate: Flammable
Ethylene carbonate: Irritating
Ethyl methyl carbonate: Flammable and irritating
Propylene carbonate: Irritating
Tetrahydrofuran: Flammable
These electrolytes may create a sweet odor when spilled. Additives in some preparations of these electrolytes could also harbor dangers from exposure.
In addition to the solvents, Li-ion batteries use lithium salts in the electrolytes .

Lithium Bis (oxalato) Borate: Irritating
Lithium Bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) Imide: Corrosive and toxic
Lithium Hexafluoroarsenate: Toxic
Lithium Iodide: No severe hazards reported
Lithium Perchlorate: Irritating and oxidizer
Lithium Tetrafluoroborate: Corrosive and harmful
Lithium Trifluoromethane Sulfonate: Irritating
Tetraethyl-Ammonium Tetrafluoroborate: Irritating and harmful
Triethyl-Methyl-Ammonium Tetrafluoroborate: Corrosive and harmful
To prevent harm to other transported materials and those along the supply chain, you should follow all regulations for moving these hazardous materials.
Lithium-Ion Battery Supply Chain Storage and Handling
Throughout the supply chain from the acquisition of chemicals to their use in Li-ion batteries, the materials will often require storage, occasionally in the same containers used for transport.
However, it's important to note that lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to certain conditions, such as high temperatures, overcharging, or physical damage, which can lead to safety concerns.
Proper handling, storage, and charging practices are essential to ensure their safe and optimal operation.
If you are interested in China import and export shipping services, please feel free to contact us.Shawn.Liao(Mr.) Phone/Wechat/Whatsapp/Skype: +8618926970495
E-MAIL:sales04@viputrans.com
Copyright © 2003-2025 VIPU Supply Chain Logistics Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved
LOGISTICS | E-COMMERCIAL FULFILLMENT | ABOUT US | CASE | NEWS | VIDEO | CONTACT US
We will find the fastest or the cheapest way for your shipment. Please specify: where from, where to, what to ship.