Be your Logistics Department in China
Customized logistics solutions, your logistics expert in China
Customized logistics solutions, Shipping from China to the World
Tel:+8613424475220 Email:info@viputrans.com 
China's truck transport services to Russia have grown significantly, supported by well-established trade routes, bilateral agreements, and robust infrastructure. This transport mode plays a crucial role in facilitating trade between the two nations, particularly for industries like automotive, consumer goods, and machinery.
· Refrigerated Trucks: For perishable goods like food and medicine.
· Tanker Trucks: For liquids, such as chemicals or fuel.
· Flatbed Trucks: For oversized or heavy equipment.
· Hazardous Material Trucks: For dangerous goods requiring safety measures.
Popular Routes for Truck Transport to Russia
China’s truck transport to Russia involves well-established routes that leverage the geographical proximity and strong trade ties between the two countries. These routes primarily utilize road networks and border crossings, supported by logistics hubs and customs infrastructure. Here are the main routes and their characteristics:
· Starting Point: Heilongjiang Province or Inner Mongolia (e.g., Harbin, Manzhouli)
· Border Crossing: Manzhouli (China) – Zabaykalsk (Russia)
· Destination: Russian Far East and Western Russia (e.g., Moscow, St. Petersburg)
· Characteristics:
o Key Corridor: Largest land port between China and Russia.
o Goods Transported: Cars, machinery, spare parts, and consumer goods.
o Advantages: Well-developed customs facilities and rail-road integration for multimodal transport.
· Use Cases: Export of Chinese-made vehicles (e.g., BYD, Geely) and automotive parts.
· Starting Point: Heilongjiang or Jilin Provinces
· Border Crossing: Suifenhe (China) – Pogranichny (Russia)
· Destination: Vladivostok, Khabarovsk, and beyond.
· Characteristics:
o Ideal for Short Distances: Proximity to Russian Far East cities.
o Cargo: Automobiles, agricultural machinery, and industrial parts.
o Advantages: Shorter transit time to ports in the Russian Far East.
· Starting Point: Hunchun City (Jilin Province)
· Border Crossing: Hunchun (China) – Kraskino (Russia)
· Destination: Vladivostok, Nakhodka, and Ussuriysk.
· Characteristics:
o Strategic Corridor: Used for regional exports to the Russian Far East.
o Advantages: Short distances, favorable trade agreements, and well-developed road networks.
· Starting Point: Urumqi or Khorgos (Xinjiang)
· Border Crossing: Khorgos (China) – Dostyk (Kazakhstan) or Alashankou (China) – Druzhba (Kazakhstan)
· Route: Transits through Kazakhstan and into Russia.
· Destination: Western Russia, including Moscow and St. Petersburg.
· Characteristics:
o Multimodal Transport: Combines road and rail transport.
o Advantages: Efficient for large-scale shipments of vehicles and parts.
· Starting Point: Cities in Heilongjiang Province (e.g., Heihe, Fuyuan).
· Border Crossings:
o Heihe (China) – Blagoveshchensk (Russia)
o Tongjiang (China) – Nizhneleninskoye (Russia)
· Destination: Russian Far East and Siberian regions.
· Characteristics:
o Seasonal Route: Dependent on the Amur River's navigability.
o Advantages: Cost-effective for heavy cargo, such as agricultural equipment and vehicles.
· Starting Point: Manufacturing hubs in Shanghai, Guangzhou, or Shenzhen.
· Route: Goods transported north to Inner Mongolia, crossing at Manzhouli or other northern ports.
· Destination: Western and Central Russia.
· Characteristics:
o Efficient Export Path: Leverages China's domestic expressway networks.
o Goods: High-tech vehicles, luxury cars, and parts.
· Starting Point: Inner Mongolia or other northern provinces in China.
· Border Crossing: Erenhot (China) – Zamyn-Üüd (Mongolia), then to Russia.
· Route: Through Mongolia to southern Siberia or western Russia.
· Characteristics:
o Alternative Route: Useful when northern crossings are congested.
o Advantages: Shorter distances for central Russian destinations.
· Starting Point: Major Chinese ports like Shanghai, Tianjin, or Qingdao.
· Sea Route: Shipping to Vladivostok or other Russian ports.
· Road Transport: Trucks distribute goods to interior Russian cities.
· Characteristics:
o Efficient for Heavy Goods: Combines cost-effectiveness of sea transport with flexibility of trucks.
o Advantages: Suitable for large automotive shipments.
Direct truck rate: Door to door from China to Russia.
FTL Price | DAP Shenzhen | DAP Shanghai | DAP Qingdao |
MOSCOW | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
STP | US$15,700 | US$15,200 | US$14,900 |
Ekaterinburg | US$14,700 | US$14,400 | US$14,200 |
Novosibirsk | US$13,400 | US$13,200 | US$12,900 |
Krasnoyarsk | US$13,200 | US$12,900 | US$12,600 |
Irkutsk | US$12,200 | US$11,800 | US$11,500 |
Nizhny Novgorod | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
Kazan | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
Chelyabinsk | US$14,600 | US$14,200 | US$13,900 |
Ufa | US$14,800 | US$14,400 | US$14,200 |
Tula | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
Ryazan | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
Chita | US$12,200 | US$11,800 | US$11,500 |
Omsk | US$14,700 | US$14,400 | US$14,200 |
Tyumen | US$14,700 | US$14,400 | US$14,200 |
Rostov, Yaroslav | US$15,200 | US$14,900 | US$14,400 |
Maximum payload 22 tons and 90 cbm per FTL. OOG/IMO transportation check case by case. | |||
The advantage of China truck Transport to Russia
China and Russia share a long border, making truck transport a practical and efficient option for moving goods between the two countries. This proximity reduces transit times compared to shipping by sea.
There are several well-established border crossings between China and Russia, such as Manzhouli–Zabaykalsk, Suifenhe–Pogranichny, and Hunchun–Kamyshovaya. These crossings are equipped to handle significant volumes of truck traffic, facilitating smooth and efficient customs clearance.
For medium-distance routes, truck transport is often more cost-effective than rail or air freight. This is particularly true for goods that require timely delivery and for routes where infrastructure supports efficient trucking.
Trucks offer unparalleled flexibility in logistics, capable of providing direct door-to-door service without the need for intermediate handling. This reduces the risk of damage and loss, and ensures faster delivery times.
China's trucking industry is versatile, capable of transporting a wide range of goods, from consumer electronics and machinery to perishable goods and hazardous materials. Specialized trucks, such as refrigerated or tanker trucks, are available to meet specific cargo needs.
Truck transport in China is well-integrated with rail and maritime networks, allowing for seamless multimodal transport solutions. This integration is crucial for efficient supply chain management and logistics optimization.
1.Weather and Terrain
Harsh winters and challenging terrain in some regions can delay transit.
2.Customs and Regulations
Despite improvements, cross-border processes can still be complex.
3.Limited Capacity During Peak Periods
High demand during certain seasons may strain transport capacity.
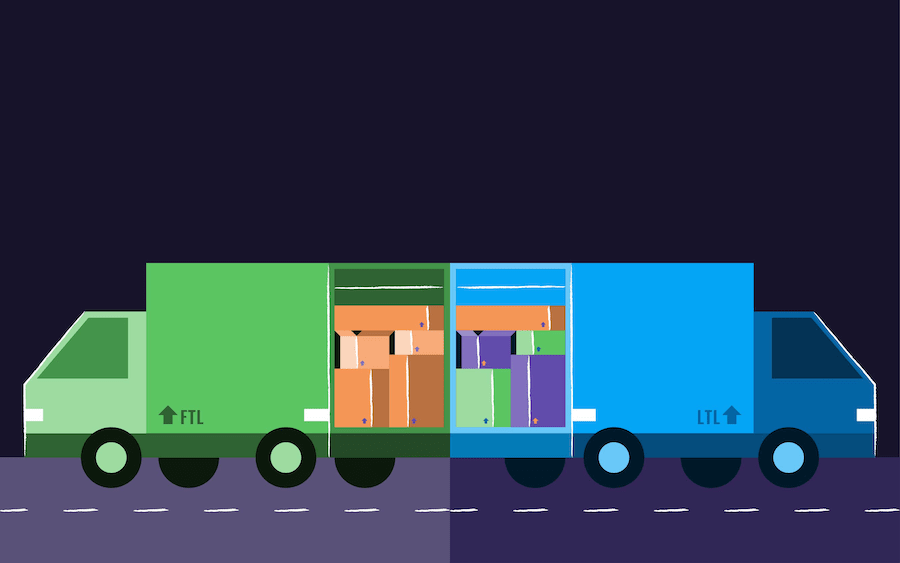
What is FTL and LTL transportation?
FTL (Full Truckload) transportation is a mode of freight shipping where an entire truck is dedicated to a single shipment or customer. It is used when the shipment volume is large enough to fill an entire truck or when a business prefers exclusive use of the vehicle for various reasons, such as minimizing transit time or ensuring better handling of goods.
1. Exclusive Use of a Truck: The truck is entirely reserved for one shipment, without sharing space with other goods.
2. Direct Delivery: The goods are transported directly from the pickup location to the destination without intermediate stops, reducing handling and transit time.
3. Ideal for Large Shipments: FTL is suitable for high-volume shipments or goods that occupy the full capacity of the truck.
4. Suitable for Sensitive Cargo: It is preferred for fragile, high-value, or temperature-sensitive goods, as the risk of damage is minimized with fewer handling points.
· Faster Delivery: Direct transit ensures quicker delivery times compared to shared transportation like Less-than-Truckload (LTL).
· Lower Risk of Damage: Limited handling reduces the chance of goods being damaged or lost.
· Cost-Effective for Large Volumes: For shipments that fill most or all of the truck, FTL often becomes more economical than splitting loads or using multiple LTL shipments.
· Customization: FTL services can be tailored to the shipper’s requirements, such as specific routes or time-sensitive deliveries.
· When the shipment size is large (typically over 10,000 pounds or 15+ pallets).
· When the cargo is fragile, hazardous, or high-value and requires extra care.
· When fast, direct delivery is essential.
· When consolidating multiple smaller shipments into one large shipment for cost-efficiency.
LTL (Less-than-Truckload) transportation is a shipping method where multiple shippers share space in a single truck, each paying only for the portion of the truck their shipment occupies. It is ideal for smaller shipments that do not require the full capacity of a truck.
1. Shared Truck Space: Multiple shipments from different shippers are consolidated in the same truck.
2. Cost Efficiency: Shippers pay only for the portion of space and weight their cargo occupies, making it more affordable than booking an entire truck for small loads.
3. Frequent Stops: Trucks make multiple stops to pick up and deliver shipments along the route.
4. Weight Range: LTL shipments typically range from 150 to 10,000 pounds or 1 to 6 pallets.
· Cost Savings: Since multiple shippers share the truck, the cost of transportation is distributed, making it economical for small loads.
· Flexibility: LTL is suitable for businesses that need to ship smaller quantities regularly.
· Eco-Friendly: Consolidating shipments reduces the number of trucks on the road, lowering overall emissions.
· Tracking and Visibility: Most LTL carriers offer real-time tracking, providing visibility into the shipment's progress.
· Longer Transit Times: Due to multiple stops for pickups and deliveries, LTL can take longer than Full Truckload (FTL) shipping.
· Higher Risk of Damage: With more handling points during consolidation and deconsolidation, there’s a slightly increased risk of damage.
· Limited Control Over Routes: Unlike FTL, shippers cannot dictate the truck’s route or schedule.
· When the shipment is smaller and does not justify the cost of a full truckload.
· When cost-efficiency is more important than speed.
· When businesses ship regularly in smaller volumes, such as e-commerce products or non-perishable goods.
Aspect | LTL (Less-than-Truckload) | FTL (Full Truckload) |
Volume | Small (150–10,000 lbs) | Large (10,000+ lbs or full truck) |
Cost | Shared, lower for small loads | Higher for small loads but cost-efficient for large loads |
Transit Time | Longer due to multiple stops | Shorter with direct delivery |
Handling | More handling, higher damage risk | Minimal handling, lower damage risk |
1.Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
Continued investment in road and border infrastructure to improve efficiency.
2.Green Logistics
Adoption of electric and eco-friendly trucks for cross-border transport.
3.Expansion of Digital Solutions
Enhanced platforms for real-time booking, tracking, and customs processing.
4.Increased Demand for E-Commerce Logistics
Growing online trade between China and Russia will boost small-scale road shipments.
If you have goods that you want to transport from China to Russia by truck, please feel free to contact us.
Lora Yang E-mail: sales02@viputrans.com SKYPE|WECHAT|WHATSAPP|MOB:+86 13424468029
Copyright © 2003-2026 VIPU Supply Chain Logistics Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved
LOGISTICS | E-COMMERCIAL FULFILLMENT | ABOUT US | CASE | NEWS | VIDEO | CONTACT US
We will find the fastest or the cheapest way for your shipment. Please specify: where from, where to, what to ship.