Be your Logistics Department in China
Customized logistics solutions, your logistics expert in China
Customized logistics solutions, Shipping from China to the World
Tel:+8613424475220 Email:info@viputrans.com 
The procurement and transportation process from China to Singapore is a well-established trade route. Singapore is one of China's largest trading partners, and the logistics infrastructure between the two countries is highly efficient. The process can be broken down into two main phases: Procurement and Logistics & Transportation.
Procurement in China
This involves sourcing and purchasing goods from Chinese suppliers.
1. Sourcing Suppliers:
Online B2B Platforms: The most common method. Key platforms include:
Alibaba.com: The largest global B2B platform. Look for suppliers with "Gold Supplier" status and "Trade Assurance" for payment protection.
1688.com: Alibaba's domestic Chinese platform (in Mandarin). Prices are often lower, but it's better suited for those with a local agent.
Made-in-China.com: Another major platform with a wide range of manufacturers.
Global Sources: Known for electronics and hardware.
Trade Shows: Attending fairs like the Canton Fair (China Import and Export Fair) is an excellent way to meet suppliers in person, see product quality, and negotiate deals.
Sourcing Agents: Hiring a reliable sourcing agent in China can save time, handle quality control, negotiate better prices, and manage supplier relationships. This is highly recommended for newcomers.
2. Due Diligence & Verification:
Company Verification: Check the supplier's business license .
Sample Evaluation: Always request a production sample before placing a large order to check for quality, specifications, and workmanship.
Factory Audit: For large orders, consider hiring a third-party inspection company (like SGS, Bureau Veritas, or AsiaInspection) to audit the factory's production capacity and quality management systems.
3. Negotiation & Contract:
Clearly agree on Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, CIF - see logistics section below). This defines who is responsible for costs and risks at each stage.
Detail product specifications, quality standards, payment terms, delivery timeline, and packaging requirements in a Proforma Invoice (PI) or formal contract.
4. Payment:
Common methods include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) with a deposit (e.g., 30%) and the balance paid before shipment or against a copy of the Bill of Lading.
Letter of Credit (L/C) is used for larger transactions, offering more security for both parties but with higher bank fees.
Avoid paying 100% upfront.
Logistics & Transportation from China to Singapore
Key Incoterms to Understand:
EXW (Ex-Works): You are responsible for everything from the supplier's door. You arrange all China-side haulage, customs, and shipping.
FOB (Free On Board): The supplier gets the goods to the port of departure and loaded on the ship. You are responsible for the main freight, insurance, and all costs in Singapore. This is very common.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The supplier arranges and pays for the main sea freight and insurance to the port in Singapore. You handle all costs upon arrival (e.g., port fees, customs clearance, delivery to warehouse).
Method | Best For | Transit Time | Key Considerations |
Air Freight | High-value, low-volume, urgent goods. | 1-3 days | Fast but expensive. Charged by volumetric weight (LxWxH/6000) or actual weight. |
Sea Freight (LCL) | Less than Container Load. Smaller shipments. | 7-14 days | Cost-effective for larger volumes. Your goods share a container with others. |
Sea Freight (FCL) | Full Container Load. Large volume orders. | 7-14 days | Most economical for large volumes. You pay for the entire container (20ft or 40ft). |
Courier (DHL, FedEx) | Very small parcels and documents. | 2-4 days | Door-to-door convenience, simple paperwork, but high cost per kg. |
Transportation Methods from China to Singapore
(1) Sea Freight
Main Ports in China: Shanghai, Ningbo, Qingdao, Shenzhen, Xiamen, Guangzhou.
Arrival Ports in Singapore: Port of Singapore (PSA, Tuas Mega Port).
Transit Time: around 5–9 days depending on origin port.
Services:
FCL (Full Container Load) – suitable for bulk shipments.
LCL (Less than Container Load) – cost-effective for small shipments.
Advantages: lowest cost per unit, stable schedules, ideal for bulk imports.
(2) Air Freight
Main Airports in China: Shanghai Pudong (PVG), Guangzhou Baiyun (CAN), Shenzhen (SZX), Beijing Capital (PEK), Hong Kong (HKG).
Arrival Airport: Singapore Changi Airport (SIN).
Transit Time: 1–3 days (direct flights are available daily).
Advantages: fastest option, reliable for high-value goods, e-commerce products, and time-sensitive shipments.
Note: Higher freight rates compared to sea freight.
(3) Rail + Sea / Truck + Sea (Multimodal Transport)
Cargo can be moved from inland Chinese provinces (e.g., Chengdu, Chongqing, Zhengzhou) by railway or trucking to coastal ports, then shipped by sea to Singapore.
Useful when supplier factories are located away from coastal hubs.
(4) Courier / Express
Carriers: DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT, SF Express.
Transit Time: 2–5 days door-to-door.
Suitable for samples, urgent small orders, e-commerce parcels.
The Shipping Process (Sea Freight Example):
Hire a Freight Forwarder: A good forwarder based in China or Singapore will handle the entire process for you. They will book space with shipping lines, arrange trucking, and prepare documents.
Haulage: Goods are transported from the factory to the Chinese port (e.g., Shenzhen, Ningbo, Shanghai).
Customs Export Declaration: Your forwarder or supplier handles Chinese export customs.
Ocean Transport: Goods are shipped to Singapore's port (PSA Singapore is one of the busiest in the world).
Import Customs Clearance in Singapore: This is a critical step. Your forwarder's Singapore partner will handle this using key documents.
Last-Mile Delivery: Goods are unloaded from the port and delivered to your specified address in Singapore.
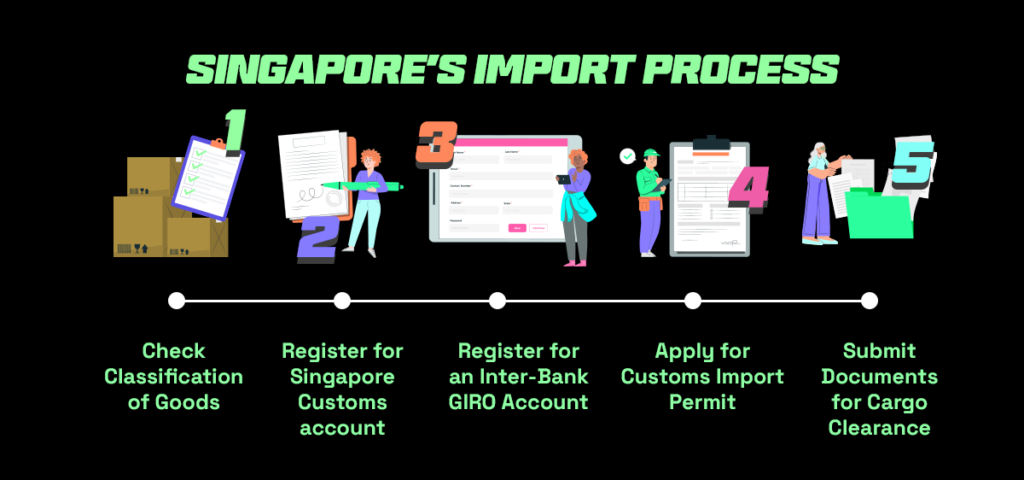
Customs Clearance in Singapore
Required Documents :
Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): The title of goods and contract of carriage.
Commercial Invoice: Details the value of the goods for duty assessment.
Packing List: Itemizes contents, quantities, and weights of each package.
Certificate of Origin (COO): May be required to determine tariff rates. A China-Singapore Free Trade Agreement (CSFTA) COO can allow for duty-free entry for eligible products.
Import Permit: Must be obtained from Singapore Customs, typically applied for by a licensed declaring agent (your freight forwarder).
Duties and Taxes in Singapore:
Goods and Services Tax (GST): 9% is levied on the CIF value (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) of the goods. This is almost always applicable.
Duty: Singapore is a free port. There is no import duty on most products. Exceptions include alcoholic beverages, tobacco products, motor vehicles, and petroleum products.
Why Work with Viputrans?
Procurement Support: Assistance in supplier verification, sourcing, and consolidation from multiple factories.
Flexible Transport Options: Choose between air, sea, express, or multimodal based on urgency and cost.
End-to-End Solutions: From supplier pickup in China, export customs clearance, international freight, Singapore customs, and final delivery.
Cost Optimization: Combine LCL shipments, negotiate bulk air rates, or provide DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) service for hassle-free imports.
If you need Viputrans to help you purchase goods in China and transport to Singapore, please feel free to contact us.
Lora Yang E-mail: sales02@viputrans.com SKYPE|WECHAT|WHATSAPP|MOB:+86 13424468029
Copyright © 2003-2026 VIPU Supply Chain Logistics Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved
LOGISTICS | E-COMMERCIAL FULFILLMENT | ABOUT US | CASE | NEWS | VIDEO | CONTACT US
We will find the fastest or the cheapest way for your shipment. Please specify: where from, where to, what to ship.